
Abstract
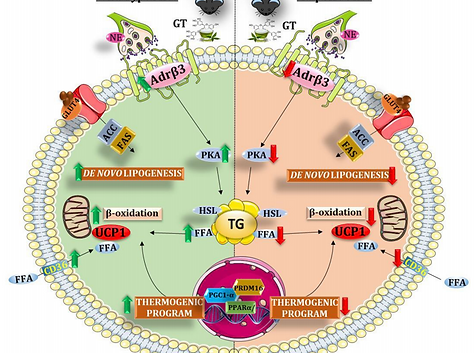
The potential contribution of green tea (GT) to the development of thermogenic/beige cells have been scarcely investigated. Here we investigated if the beneficial effects of GT in the induction of thermogenic/beige adipocytes results from an initial cell commitment during adipogenesis. Male C57Bl/6 mice (3 months) were divided into 3 groups: Control (chow diet), Obese (cafeteria diet), and Obese + GT. Mice received GT gavage (500 mg/kg of BW) over 12 weeks (5 days/week), after 4 weeks of diet, totalizing 16 weeks of experimentation. GT treatment increased energy expenditure (EE) in mice fed with cafeteria-diet leading to reduced BW gain, decreased adiposity, reduced inflammation, and improving insulin sensitivity. Those phenotypes were associated with enhanced expression of oxidative, thermogenic and beige genes. GT induced a futile cycle through de novo lipogenesis activating the thermogenic pathway. Induction of beige phenotype occurs autonomously in adipocytes and involves the PPARγ/FGF21/AMPK/UCP1 pathway. Our study identified that metabolic changes caused by GT may involve the temporal expression of PPARγ promoting the induction of thermogenic cells by reprogramming initial steps of adipocyte commitment.
Bolin AP, Sousa-Filho CPB, Marinovic MP, Rodrigues AC, Otton R. Polyphenol-rich green tea extract induces thermogenesis in mice by a mechanism dependent on adiponectin signaling. J Nutr Biochem. 2020 Apr;78:108322. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.108322. Epub 2019 Dec 11. PMID: 32120266.
Abstract
Adiponectin is downregulated in obesity negatively impacting the thermogenesis and impairing white fat browning. Despite the notable effects of green tea (GT) extract in the enhancement of thermogenesis, if its effects are being mediated by adiponectin has been scarcely explored. For this purpose, we investigated the role of adiponectin in the thermogenic actions of GT extract by using an adiponectin-knockout mice model. Male wild-type (WT) and knockout (AdipoKO) C57Bl/6 mice (3 months) were divided into 6 groups: mice fed a standard diet+gavage with water (SD WT, and SD AdipoKO), high-fat diet (HFD)+gavage with water (HFD WT, and HFD AdipoKO), and HFD + gavage with 500 mg/kg of body weight (BW) of GT extract (HFD + GT WT, and HFD + GT AdipoKO). After 20 weeks of experimentation, mice were euthanized and adipose tissue was properly removed. Our findings indicate that treatment with GT extract reversed complications of obesity in WT mice by decreasing final BW gain, adiposity index, adipocyte size and insulin resistance (IR). However, the action of the GT extract was not effective in reversing those markers in the AdipoKO mice, although GT acts independently in the reversal of IR. GT-treatment induced enhancement in energy expenditure (EE), BAT thermogenesis, and promoted browning phenotype in the subcutaneous WAT (scWAT) of WT mice. On the other hand, the thermogenic program was markedly impaired in BAT and scWAT of AdipoKO mice. Our outcomes unveiled adiponectin as a key direct signal for GT extract inducing adaptive thermogenesis and browning in scWAT.
Bondan EF, Cardoso CV, Martins MFM, Otton R. Memory impairments and increased GFAP expression in hippocampal astrocytes following hypercaloric diet in rats. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2019 Sep 23;77(9):601-608. doi: 10.1590/0004-282X20190091. PMID: 31553389.
Abstract
Objective: Hypothalamic inflammation and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) overexpression in astrocytes are well described in obese animals, as are some cognitive and memory deficits. As the hippocampus plays important roles in the consolidation of information, this investigation aimed to observe the memory function and the astrocyte expression of GFAP in the hippocampus of rats that received either a hypercaloric or a normocaloric diet.
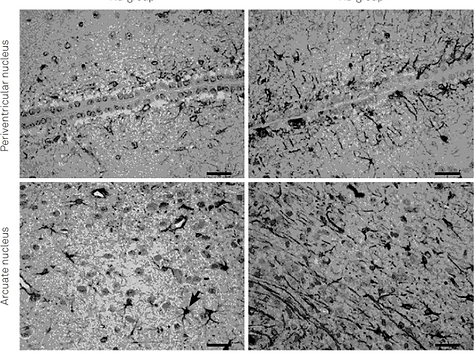
Methods: Adult male Wistar rats received a high-fat (cafeteria) or a standard diet for 60 days. On the 61st day, the rats were submitted to the novel object recognition (NOR) test at three and 24 hours after the first contact with objects, to assess short-term and long-term memory, respectively. Thereafter, the rats were euthanized and their brains were collected for GFAP immunohistochemical investigation in the hippocampus (CA1, CA2, CA3 areas) and hypothalamus (periventricular and arcuate nuclei). Astrocytic reactivity was assessed by morphometry. Different white adipose tissue depots and brown adipose tissue were weighed to calculate the adiposity index.
Results: The hypercaloric diet increased body weight gain, adiposity index, white adipose tissue weight (epididymal, subcutaneous and retroperitoneal) and brown adipose tissue weight. Rats fed with the hypercaloric diet showed short-term and long-term memory impairments in the NOR test, as well as increased GFAP expression in astrocytes from all analyzed hypothalamic and hippocampal areas.
Conclusion: This astrogliosis suggests that the neuroinflammatory response also occurs in the hippocampus and may be involved in the memory losses observed in obese/overweight animals.

Polyphenol-rich green tea extract improves adipose tissue metabolism by down-regulating miR-335 expression and mitigating insulin resistance and inflammation.
Otton, R., Bolin, A. P., Ferreira, L. T., Marinovic, M. P., Rocha, A. L. S., & Mori, M. A. (2018). Polyphenol-rich green tea extract improves adipose tissue metabolism by down-regulating miR-335 expression and mitigating insulin resistance and inflammation. The Journal of nutritional biochemistry, 57, 170-179.
Abstract
Obesity leads to changes in miRNA expression in adipose tissue, and this modulation is linked to the pathophysiology of the disease. Green tea (GT) is a natural source of polyphenols that have been shown to confer health benefits, particularly preventing metabolic diseases. Here, we investigated if the beneficial effects of GT in obesity results from changes in the miRNA profile in white adipose tissue. GT treatment [500 mg/body weight (BW)/12 weeks] increased energy expenditure of high-fat diet-fed mice (16 weeks), leading to reduced weight gain, decreased adiposity, reduced inflammation and improved insulin sensitivity. These phenotypes were associated with a decrease in the expression of miR-335 in the adipose tissue. miR-335 was up-regulated by TNF-α in adipocytes and, in turn, down-regulated genes involved in insulin signaling and lipid metabolism. On the other hand, GT inhibited TNF-α effect. In conclusion, miR-335 serves as a link between inflammation and impaired metabolism in adipose tissue, providing an important mechanistic insight into the molecular basis underlying GT action during obesity.

Redox status on different regions of the central nervous system of obese and lean rats treated with green tea extract.
Macedo RC, Bondan EF, Otton R Redox status on different regions of the central nervous system of obese and lean rats treated with green tea extract.Nutr Neurosci. 2017 Jul 31:1-13
Abstract
OBJECTIVES:
The purpose of this study was to evaluate some indicators of redox status, and inflammation on different regions of the central nervous system (CNS) of obese rats treated with green tea (GT). We hypothesized that obesity could affect the redox balance in different brain regions due to the diverse nature of the cells as well as the selective neuronal vulnerability to oxidative stress, and GT could triggers benefits effects restoring the redox status.
METHODS:
Male Wistar rats were treated with GT by gavage (12 weeks/5 days/week; 500 mg/kg of body weight) and obesity was induced by cafeteria diet (8 weeks). After this period, the animals were killed and brain tissue (cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and brainstem) was removed to evaluate oxidative stress and inflammation (cytokine release).
RESULTS:
We showed that the cafeteria diet had little effect on redox balance in the cerebral cortex and cerebellum; however, the brainstem was the region of the CNS most sensitive to cafeteria diet-induced redox unbalance. GFAP expression was increased in the cerebral cortex of obese rats and reduced by GT. It was also evident that GT treatment had numerous beneficial effects against oxidative damage to biomolecules in all brain regions analyzed.
DISCUSSION:
Our study established that different CNS regions show selective neuronal vulnerability when exposed to a diet enriched with fats and sugars, and the beneficial effect of GT was similar among these regions. We conclude that GT could be a good strategy for improving and maintaining brain function under healthy and pathological conditions.

Abstract
Our goal was to establish the requirement of β3 adrenoceptor (β3Adr) for green tea (GT) effects on the energy metabolism of obese mice. This study was carried out in wild-type (WT) and β3Adr knockout (KO) male mice fed with a standard diet or a high-fat diet (HFD/16 weeks) treated or not with GT (0.5 g/kg of body weight (BW)/12 weeks). GT-treatment attenuated final BW, BW gain, and adiposity index increased by HFD, improving insulin resistance (IR) and FGF21 level, without changing the food intake of WT mice. GT-treatment of β3AdrKO mice attenuated only IR, denoting GT-effects independent of β3Adr. We observed increased lipolysis accompanied by decreased adipocyte size in white adipose tissue (WAT) as well as browning of the subcutaneous WAT induced by GT in a way dependent on β3Adr. In brown adipose tissue (BAT) mRNA levels of lipolytic/oxidative genes, including β3Adr/Ucp1 and energy expenditure (EE) was increased by GT dependent on β3Adr. GT-treatment increased adiponectin independent of β3Adr. Also, independent of β3Adr pathway GT promoted an increase in β2Adr/Ucp1 mRNA levels and EE in BAT whereas; in the liver, GT has a dual role in increasing lipid synthesis and oxidation. These data lead us to suggest that GT uses β3Adr pathway activation to achieve some of its beneficial health effects.

Torres LF, Cogliati B, Otton R. Green Tea Prevents NAFLD by Modulation of miR-34a and miR-194 Expression in a High-Fat Diet Mouse Model. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Dec 4;2019:4168380. doi: 10.1155/2019/4168380. PMID: 31885789; PMCID: PMC6914886.
Abstract
Background/aims: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is considered the hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome. It is currently the most common chronic liver disease with complex pathogenesis and challenging treatment. Here, we investigated the hepatoprotective role of green tea (GT) and determined the involvement of miRNAs and its mechanism of action.
Methods: Male C57Bl/6 mice were fed with a high-fat diet for 4 weeks. After this period, the animals received gavage with GT (500 mg/kg body weight) over 12 weeks (5 days/week). HepG2 cell lines were transfected with miR-34a or miR-194 mimetics and inhibitors to validate the in vivo results or were treated with TNF-α to evaluate miRNA regulation.
Results: GT supplementation protects against NAFLD development by altering lipid metabolism, increasing gene expression involved in triglycerides and fatty acid catabolism, and decreasing uptake and lipid accumulation. This phenotype was accompanied by miR-34a downregulation and an increase in their mRNA targets Sirt1, Pparα, and Insig2. GT upregulated hepatic miR-194 by inhibiting TNF-α action leading to a decrease in miR-194 target genes Hmgcs/Apoa5.
Conclusion: Our study identified for the first time that the beneficial effects of GT in the liver can be due to the modulation of miRNAs, opening new perspectives for the treatment of NAFLD focusing on epigenetic regulation of miR-34a and miR-194 as green tea targets.
Marin DP, Astorino TA, Martinatto F, Ragazzini FT, Bispo RE, Foschini D, Otton R. Comparison of perceptual responses between different upper-body sprint interval exercise protocols. Physiol Behav. 2019 Oct 15;210:112626. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2019.112626. Epub 2019 Jul 22. PMID: 31344392.
Abstract
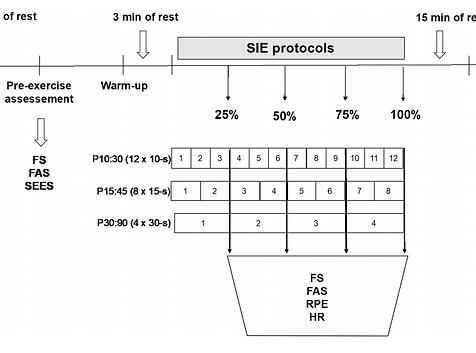
This study examined the perceptual responses to various upper-body sprint interval exercise (SIE) protocols matched for total work and work/rest ratio. Fourteen active men (24 ± 4 years, BMI = 26.2 ± 2.7 kg/m2, body fat = 11.5 ± 4.4%) participated in 3 all-out SIE protocols consisting of battling rope exercise: P10:30 (12 × 10-s bouts with 30-s recovery); P15:45 (8 × 15-s bouts with 45 s recovery); and P30:90 (4 × 30-s bouts with 90-s recovery). During exercise, affective valence (FS +5 to -5), arousal (FAS 1-6), rating of perceived exertion (RPE 6-20), and heart rate (HR) were assessed. Post-exercise, enjoyment, self-efficacy, and intentions were measured. Results revealed a significant decline in FS (p = .02; partial eta squared [η2p] = 0.27) and a progressive increase in FAS (p = .001; η2p = 0.86), RPE (p = .001; η2p = 0.88), and HR (p = .001; η2p = 0.94), but no protocol X time interaction. Affective valence reached a nadir at values equal to -0.36 ± 3.41 (Cohen's d = -0.49), -0.43 ± 3.75 (Cohen's d = -0.44), and - 0.93 ± 3.49 (Cohen's d = -0.56) in response to P10:30, P15:45, and P30:90, respectively. There were no differences between protocols for enjoyment, intention, or self-efficacy. A negative relationship exhibited between FS and RPE was moderated by participants' tolerance of exercise intensity (β = 1.84, p < .05). Further, the association between FS and future intention was mediated by self-efficacy. Overall, upper-body SIE protocols exhibit similar perceptual responses when volume and work to rest ratio (1:3) are matched. Tolerance of exercise intensity may be used to predict changes in FS during SIE.

Green Tea Extract Reverts Obesity-Related Dysfunction by Remodeling White Adipose Tissue Metabolism an AMPK-dependent mechanism.
ROCHA, A. L. S. ; BOLIN, A. P. ; CARDOSO, CAL ; OTTON, ROSEMARI . Green Tea Extract Reverts Obesity-Related Dysfunction by Remodeling White Adipose Tissue Metabolism an AMPK-dependent mechanism. pp 1-14First online: 11 September 2015 European Journal of Nutrition.
Abstract
Purpose: Beneficial effects of green tea polyphenols against obesity have been reported. However, until this moment the molecular mechanisms of how green tea can modulate obesity and regulates fat metabolism, particularly in adipose tissue, remain poorly understood. The aim of this study was to evaluate the role of green tea extract in the adipose tissue of obese animals and its effect on weight gain, metabolism and function (de novo lipogenesis and lipolysis) and the involvement of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation. Methods and Results: Here, we show that obese-induced rats with cafeteria diet ( 8 weeks) that were treated with a green tea extract (500 mg/kg of body weight) for 12 weeks, showed a significant reduction in indicators of obesity such as hyperlipidemia, fat synthesis, body weight and fat depots through activation of AMPK as compared with control standard diet. AMPK was induced in adipose tissue of animals that were treated with green tea and restored insulin sensitivity, increased mRNA expression of GLUT4, reducing the concentrations of plasma and liver lipid content, also stimulating fatty acid oxidation in the adipose tissue. Importantly, AMPK represses de novo lipogenesis in adipose tissue, but also reverted lipid droplets in the liver and the development of insulin resistance in diet-induced obese rats.
Green tea polyphenols change the profile of inflammatory cytokine release from lymphocytes of obese and lean rats and protect against oxidative damage.
MOLINA, N.; Bolin, A.P.; OTTON, R. Green tea extract changes the profile of inflammatory cytokine release from lymphocytes of obese and lean rats and protects against oxidative damage. Volume 28, Issue 2, October 2015, Pages 985–996 International Immunopharmacology (Print), 2015.
Abstract
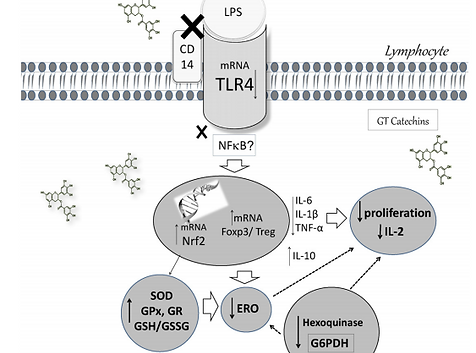
This study aimed to investigate whether green tea polyphenols (GT) modulate some functional parameters of lymphocytes from obese rats. Male Wistar rats were treated with GT by gavage (12 weeks/5 days/week; 500 mg/kg of body weight) and obesity was induced by cafeteria diet (8 weeks). Lymphocytes were obtained from mesenteric lymph nodes for analyses. In response to the cafeteria diet we observed an increase in activity of the metabolic enzyme hexokinase, ROS production, MnSOD, CuZnSOD and GR enzyme activities and proliferation capacity of the cells (baseline), whereas IL-10 production was decreased. Obese rats treated with GT decreased cell proliferation (under ConA stimulation). Hexokinase and G6PDH activity, ROS production and MnSOD, CuZnSOD, GPx and GR enzymes remained increased, accompanied by an increase in Nrf2 mRNA level. There was a decrease in pro-inflammatory IL-2, IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α cytokines that were accompanied by a decrease in the mRNA level of TRL4 while IL-10 production was increased in obese rats treated with GT. GT treatment of lean rats showed similar results to that of obese rats treated with GT, indicating that the effects of GT are independent of diet. Foxp3 and IRF4 mRNA levels were increased by GT. In conclusion, cafeteria diet modulated the function of lymphocytes from lymph nodes, increasing ROS production and decreasing anti-inflammatory IL-10, which could contribute to the inflammatory state in obesity. GT reduced ROS production, improving the redox status and reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine production by lymphocytes, suggesting that GT treatment may be driving lymphocytes to a more anti-inflammatory than pro-inflammatory microenvironment.
